Lesson 2: Refraction and Total Internal Reflection
When light is incident on a transparent material such as glass or water, some of the light is reflected from the surface. The rest of tehe light is transmitted through the material. We have refraction if the direction of transmitted rays is different from the direction of the incident rays. Total internal reflection is said to occur when light encounters a boundary between a medium of a higher index of refraction and one with a lower index of refraction.
|
•HOOK:
Show the students this Youtube video on Reflection of light and total internal reflection. Ask them to write down their observation and discuss it in their group. •ACTION: Discuss refraction, refraction index, Snell’s law, lasers and total internal reflection with the class. Appropriate equations (including Snell's law) should be derived. The students watch YouTube video on dispersion •CONSOLIDATION: Solve one problem using the Snell’slaw and gives the student two other problems to solve in groups. See PROBLEMS. The solutions can be used as exit cards for the groups 
Fig. 4: Snell's law Source: www.Google.ca |
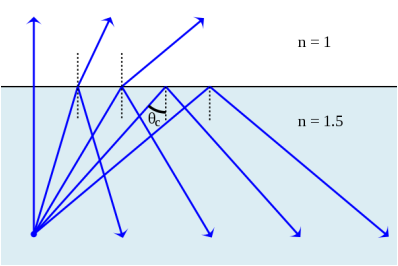

Fig. 6:Snell
Source: www.Google.ca |
